Contents [show]
Nonmelanoma skin cancer is the better-known type of skin cancer. It is called non-melanoma, because this group of tumors includes all types of skin cancer, except one: Malignant melanoma. Which is cancer that develops from melanocytes.
If you want to know about typical skin disorders then click the link given below:
All About Typical Skin Disorders
Causes Of Skin Cancer
Genetic predisposition is the main reason for the presence of skin cancer. Although there are other well-identified aspects that also intervene. Such as ultraviolet radiation, some chemical agents, human papillomavirus infections and even immunosuppression. Transplanted patients have a higher incidence of skin cancer than the normal population.
The most frequent causes are:
- The exposure excessive ultraviolet radiation(UV), whose primary source is sunlight. The degree of exposure to this radiation depends on the intensity of the light, on the exposure time and on whether the skin has been protected. People who live in areas where they exposed to intense sunlight. All year they are at greater risk of developing this type of cancer. In addition, being outdoors for long periods of work or leisure without protecting yourself with appropriate clothing and sun protection increases the possibility of developing it.
- The tanning booths and lamps are other origins of ultraviolet radiation that may increase the danger of developing skin cancer non – melanoma.
- The exposure to certain chemicals such as industrial tar, arsenic, coal, paraffin and different types of oils.
- The exposure to radiation, such as produced by radiation.
- Serious or prolonged lesions or inflammations of the skin, such as severe burns, the skin covering the area where a serious bone infection occurred and skin damaged by certain inflammatory diseases.
- The treatment of psoriasis with psoralen and ultraviolet light administered to some patients with psoriasis.
- The xeroderma pigmentosum, a unique inherited disorder, lower the capability of the skin to repair the damage to DNA as a result of exposure to sunlight. People who have this disorder promote a large number of skin tumors, sometimes from childhood.
- The nevus syndrome, basal cell is a rare congenital condition, which causes multiple basal cell malignancies (basaliomas). Most cases, although not all, are hereditary.
Read Also: Lose Cheek Fat – Best Way To Lose Face Fat
Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Nonmelanoma skin cancer may have the appearance of various skin tags. The main warning signs are the appearance of a new mass, a spot or bump that is growing (over the course of a few months or one to two years), or an ulcer that does not heal within three months.
“The symptoms of this cancer are very variable. We find from continuous growth cysts, ulcers that do not heal, scars that increase, corneal excrescences (cutaneous horn) and especially moles that change shape or begin to show displeasure such as pain, itching, bleeding, etc.
The most common are:
- The basal cell carcinomas emerge somewhat flat area, as goofy that becomes reddish, or small waxy, glossy and translucent to focal point areas which may bleed a minor injury. In these areas, it is familiar to spot one or more visible irregular blood vessels, or show areas of brown, blue or black.
- The squamous cell carcinoma may occur as growing lumps, often rough, flat or reddened patches of skin that grow slowly surface. These two types of non-melanoma skin cancer can expand on a flat surface that only shows slight changes from normal skin.
- The Kaposi sarcoma usually begins in a small area like that acquires a purple color becomes a tumor.
- The mycosis fungoides start as a rash, often in the buttocks, hips or lower abdomen. It may look like a skin allergy or other type of irritation.
- The tumors of the annexes appear as bumps inside the skin.
- The Skin sarcomas appear as large lumps under the surface thereof. Merkel cell tumors usually appear in the form of purple-red nodules or ulcers (sores) located on the face, or, less frequently, on the arms or legs.Read Also: why are omega-3 fatty acids important – why do we need omega-3
Prevention From Skin Cancer
The most important way to reduce the risk of developing nonmelanoma skin cancer is to avoid exposing yourself to sun rays and other sources of ultraviolet light.
The easiest way to avoid excessive exposure to ultraviolet light is to stay away from the sun and shade whenever possible. You are free to apply this, both in summer periods and the rest of the year. Since weather effects, such as cloud cover or snow. Do not reduce the incidence of solar radiation completely.
It is important that this precaution is taken from childhood, as it has been shown that 80 percent of the damage that the sun can cause to the skin occurs before the age of 18.
Read Also: 21 High Fiber Foods List – You Must Eat
Some recommendations to prevent the onset of this type of cancer are:
Protect yourself with clothes
Wearing a shirt and a wide-brimmed hat allows increased protection against solar radiation. Generally, tightly woven fabrics also offer better protection.
Regarding sunglasses, experts recommend using those that have an ultraviolet absorption percentage of 99 to one hundred percent, since it allows adequate protection of the eyes and the area of skin around them.
On the other hand, specialists suggest covering the most sensitive areas that are exposed to sunlight throughout the year. 85 percent of malignant tumors occur on the face, cleavage, and scalp.
Read Also: Six Essential Nutrients Which Are Important For Your Body
Sunscreen creams
Use a protective cream of factor 15 or more on skin areas exposed to the sun, particularly when the light is intense. People with fair skin and those who burn easily should apply sunscreen lotion more frequently.
For protection to be effective, protection must be applied before sun exposure and in all visible skin areas. Many sunscreen lotions lose effectiveness when the person sweats or swims and must be reapplied to offer the highest level of protection.
Experts insist that the cream should be applied even if there is a foggy day or the sky covered with light or little compact clouds since ultraviolet light can pass through them.
Do not use tanning booths
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet light may build up the risk of developing skin cancer, as it leads to skin aging. For this reason, dermatologists advise against its use
Read Also: Best Foods To Eat For Clear Skin
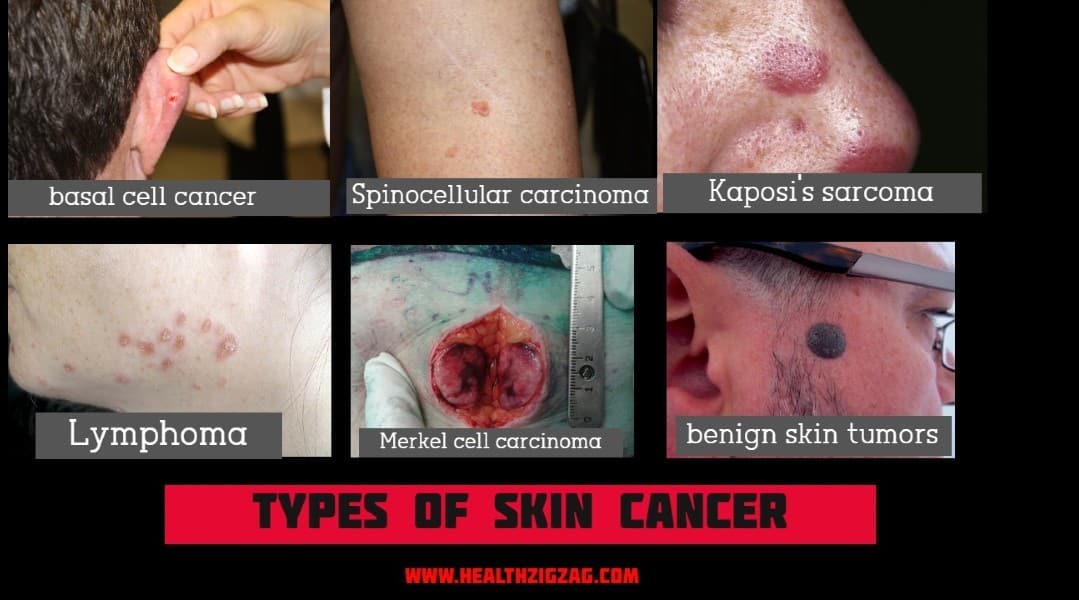
Types Of Skin Cancer
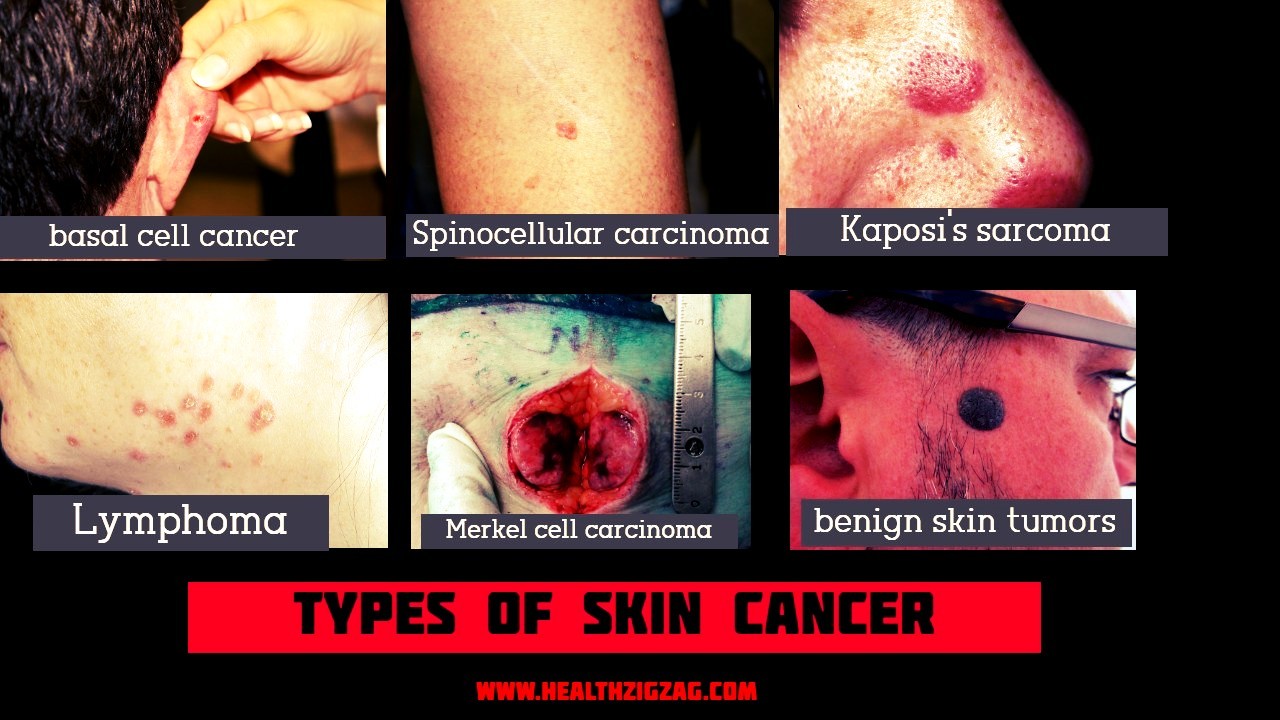
There are many types of non-melanoma skin cancer, but there are two that are the most common: basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
· Basal cell carcinoma (basal cell cancer)
It is a slow-growing tumor. It is very uncommon for a basal cancer cell to spread to different parts of the body. However, if a basal cell cancer left untreated. It can spread to nearby areas and affect the bones, as well as other skin tissues. After treatment, basal cell carcinoma may reappear in the same place on the skin.
· Spinocellular carcinoma (squamous cell carcinoma)
It develops in the upper layers of the epidermis. And accounts for about 20 percent of all cases of skin cancer. This often appears in areas of the body exposed to the sun. Such as the face, ears, neck, lips and the back of the hands. It can also develop in scars or skin ulcers in other parts of the body.
Other types of non-melanoma skin cancer, less common than the previous ones are:
- Kaposi’s sarcoma.
It originates in the dermis, but it can also form in the internal organs. It usually develops in people affected by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). - Lymphoma.
The dermis contains a considerable number of lymphocytes (a type of immune system cells). When they become malignant they form the lymphoma. Although most of these types of cancer appear to originate in the lymph nodes or internal organs. There are certain types of lymphoma that originate in the skin. The medical term “primary cutaneous lymphoma” means “lymphoma that has originated in the skin.” The most common type of primary cutaneous lymphoma is cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, also called fungoid mycosis. -
Sarcomas
Sarcomas develop from connective tissue cells, usually in tissues that lie deep beneath the skin. Less often, these can occur in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. There are several types of sarcoma that can develop on the skin including dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and angiosarcoma.
- Merkel cell carcinoma.
It develops from the endocrine cells of the skin. They often reappear after treatment and spread to nearby lymph nodes. They can also spread to internal organs. - There are also benign skin tumors. Most of them are not cancerous, and only rarely do they become cancer. Among these tumors are most types of moles, seborrheic keratoses (raised spots, brown, brown or black with a “waxy” texture or a rough surface), hemangiomas (benign tumors of blood vessels) , lipomas (soft tumors of benign fat cells) and warts (rough surface tumors caused by a virus).
Precancerous Diseases
- Actinic keratosis:
Precancerous skin condition caused by exposure to sunlight. They are small rough spots that can be red, pink or skin color. They usually develop on the face, ears, backs of the hands and arms of middle-aged or older people. Who have light skin, although they can also appear in other areas of the skin exposed to the sun. Generally, people who have actinic keratosis will develop many more. They usually grow slowly and cause no more symptoms or signs than skin blemishes. It is possible, but not common, for actinic keratoses to become squamous cell cancer. They also often disappear on their own, but may reappear. - Squamous cell carcinoma in situ or Bowen’s disease:
It is the primitive form of squamous cell skin cancer. The cells of this cancer are completely inside the epidermis and have not spread to the dermis. It manifests itself in the form of reddish spots. Compared with actinic keratoses, the spots of squamous cell carcinoma in situ are usually larger. Often more than half a centimeter, more intense red and are more scaly and rough.
Read Also: How To Remove Wrinkles Naturally
Diagnosis Of Skin Cancer
“In the suspicion of having any lesion that is persistent over time. That changes its characteristics or that tends to grow slowly but progressively. The patient should go to the dermatologist to evaluate it and give a diagnosis.
If there is any reason to suspect that there is skin cancer. The doctor will use one or more methods to determine if the disease is actually present. The first step is to observe the size, shape, color, and texture of the area in question and whether it bleeds or flakes.
He will then examine the rest of the body to see if the patient has spots or moles that may be related to skin cancer. It may be necessary to ask other questions or other tests.
If the doctor thinks that an area could have nonmelanoma skin cancer. He or she will take a sample (biopsy) of skin from the suspected area for examination under a microscope. This method called a skin biopsy. To do this test different methods can be used.
However, it is equally effective for the patient to check the skin itself, preferably once a month. To do this, you should know the appearance of moles, imperfections, freckles and other marks that you have on the skin to be able to detect any changes.
We recommend you to do the self-examination in front of a full-length mirror. For hard-to-see areas, you can use a hand mirror. You should examine all areas, including the palms and soles of the feet, the lumbar region and the back of the legs.
Read Also: Best Benefits Of Pumpkin Seeds For Hair, Skin, And Health
Treatments For Skin Cancer
Removal is the most common treatment for this type of lesions. Which can be completed with the so-called Mohs surgery depending on the location or if the spot has a considerable size.
- The simple excision involves the removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue.
- Mohs surgery: The layer of the skin affected by the cancer is removed and subsequently. The doctor removes the tissue that surrounds the area by comparing both in the microscope.
- Cryosurgery: By means of liquid nitrogen, cancer cells are frozen and destroyed.
- Laser surgery: This method used in very superficial carcinomas on which the laser beam is applied to vaporize cancer cells.
- Electrodesiccation: the tumor removed by scraping the tissue, and then the area where the spot was treated. With an electric needle is treated to destroy the remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: The most frequently used medication is fluorouracil. Which used topically reaches the skin’s closest cells, so it will be used only in premalignant pathologies. This medicine reddens the area where you will apply it and makes it more sensitive to the sun. So it is advisable that the area is well protected.
- Radiation therapy: Consists of the use of radiation to destroy cancer cells. The treatment lasts a few minutes and is not painful.
This method used in those patients who cannot undergo surgery, such as elderly people. This therapy can cure those kinds of cancer that are in low stages. This also can be used as a complement to the surgery.
Read Also: How To Moisturize Your Face Naturally
Forecast
Nonmelanoma skin cancer curable in 90 percent of cases, If the early treatment is performed. However, there are high chances that it will reappear over time. So it is advisable to undergo regular medical exams to be able to treat it again.
When should the patient go to the specialist?
The time when patients should go to the specialist to make a consultation is “if you have any questions that your primary care physician cannot resolve.”
Read Also: How To Get A Glowing Body Skin
Read Also: Carrot Juice For Wrinkles




